A bot to help automate argo-cd changes via Github PRs.
Currently supports running diffs on open Pull Requests, check the Workflow section for more, or comment argo help on an open PR.
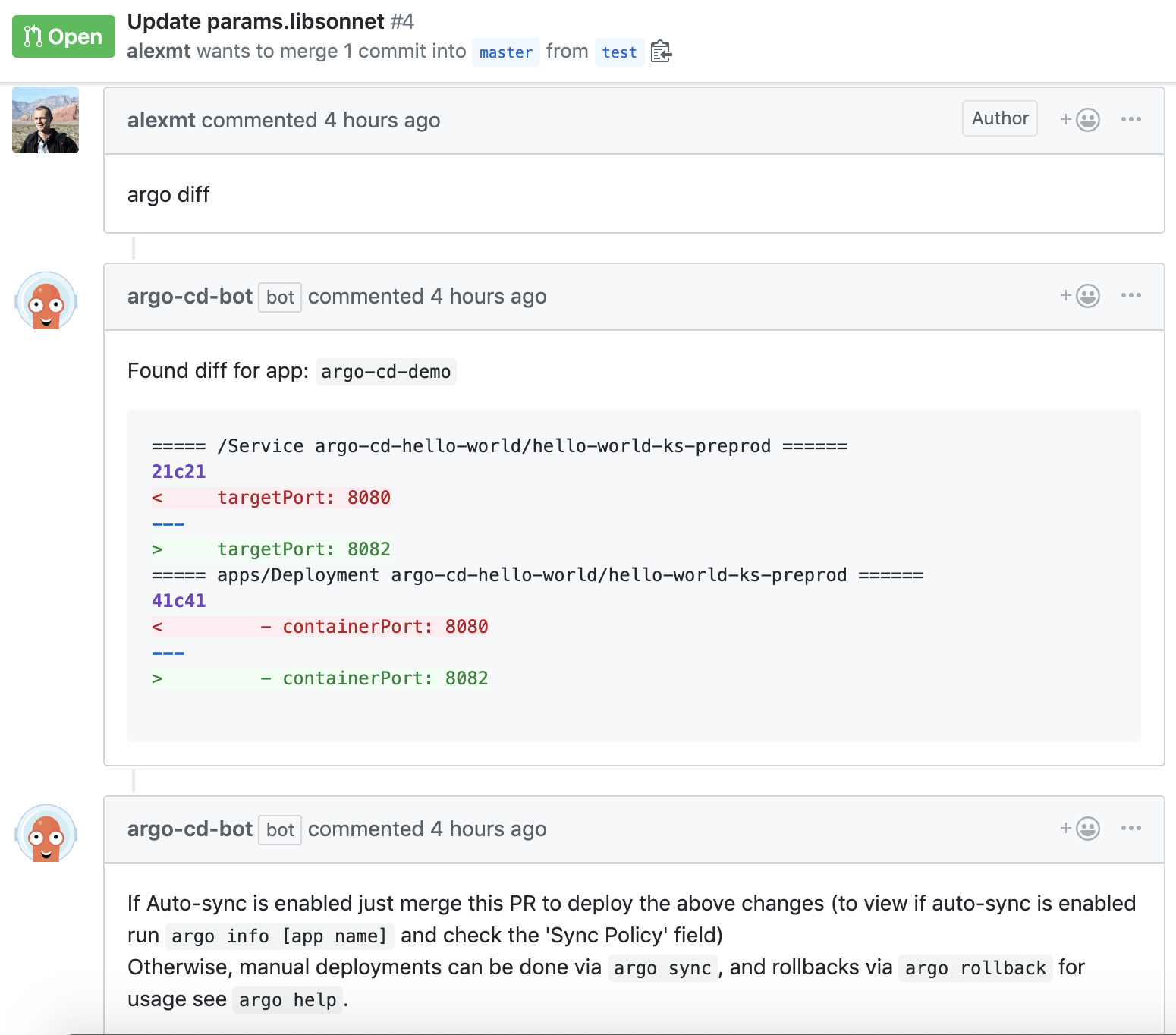
- Comment
argo diffon an open PR, to view diff between local branch and Kubernetes cluster. - PR diffs can be easily reviewed by everyone.
- Catch errors in the output of
argo diffbefore applying changes. - Comment
argo sync [app name]to deploy changes, and merge PR.
- Users can submit changes via Github (after PR approval), without needing cluster credentials.
- Audit changes made to clusters via Github PRs/server logs.
This section describes the workflow supported by the bot.
- User opens a PR in a Kubernetes repo with changes to deployment files.
- User comments with
argo diffon the PR. - Bot checks out current state of PR and runs
argocd diff --local. Diff output is posted on the PR as a comment. - Team can review code changes in the PR, and double check the posted diff.
- Author can iterate, making changes on the PR and re-comment with
argo diffonce they are ready. - Deploying Changes:
- If Auto Sync is enabled: once the PR is merged, ArgoCD server syncs it with production.
- Otherwise, user can comment
argo sync [app name]to sync changes from branch, before merging PR.
When any command is run on by a user, the PR holds a lock, until the it is merged, or unlock is run.
The PR lock prevents other users from attempting to run commands on their PRs. This is to synchronize changes on master.
i.e to prevent a scenario like this:
- Alice creates a PR, comments
diff, and she's happy with the output posted. - Bob creates a second PR, and comments
diff. - Bob merges his PR to master.
- Alice's diff output on her PR is now invalid and she might have no idea. Her merge to master, might produce a different state than what her diff had shown.
With locking in place, Bob will not be able to merge his PR until he coordinates with Alice, by either running unlock, or waiting for her PR to get merged first.
These are commands that are supported by the bot.
argo diff: this checks out the current state of the PR, queries the argoCD server at/api/v1/applicationsand diffs all applications with their current state from the PR.argo unlock: this unlocks the current PR, so other users can rundiff; see locking section above.argo sync [app name]: this syncs changes on current branchargo rollback: this rolls back latest change
More commands might be added, run argo help on a PR, to view all supported commands.
Create a new GitHub App here.
- Webhook URL, is the host where the bot will run.
- Webhook Secret, is an optional secret, make sure it matches the config (see below section)
- Private key, generate a new key and place it in the root directory, and update config below.
- Check the generated
APP_IDby Github. For more on creating Github apps see
Please give the argo-cd app the following permissions:
Read access to administration and metadata
Read and write access to commit statuses, issues, and pull requests
There is an .env_example file that should be renamed to .env. NodeJS will read that file and expose the variables to the bot, when running locally.
When running in Kubernetes, there is a helper script to create k8s secrets from that file (more on this in the kubernetes deployment section).
Here is a description of each parameter:
PORTis the port that bot will listen on via HTTP.LOG_LEVELcan be set totrace,debug,info,warn,error, orfatal.KUBECTL_EXTERNAL_DIFFthis is used byargocd diff, we pass a helper script to pretti-fy diffs posted on the PR.APP_IDis the app id corresponding to the Github app (this is generated on app creation).GHE_HOSTfor Github enterprise installations, specify the hostname. Otherwise leave blank, bot will use Github.comGITHUB_REPOthis is the repo that the bot will operate on.GITHUB_TOKENgenerate a Github token for the bot, and give it no scopes. This is just used to clone the repo.WEBHOOK_SECRETis the secret configured when creating the Github app (can be left empty if no secret is specified).PRIVATE_KEY_PATHis the path to the private key generated for the Github app, this is usually a.pemfile.ARGOCD_SERVER, this is the ip address/hostname of the argocd server.ARGOCD_AUTH_TOKENit is recommended to generate an automation token using the/api/v1/projects/{project}/roles/{role}/tokenAPI. For more information see
Docker images of argocd-bot are built here, they are provided as part of releases here
Check the config section above, once you have a .env file that's populated with the correct values run ./helper_scripts/create_kubectl_secrets.sh.
This will generated a k8s secret argocd-bot-secret used by the deployment.
Build manifests using kustomize:
npm run manifests
Create deployment from manifests:
kubectl create -f deployment/install.yaml
See docs here
See docs here