| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给你一个二叉树的根结点,返回其结点按 垂直方向(从上到下,逐列)遍历的结果。
如果两个结点在同一行和列,那么顺序则为 从左到右。
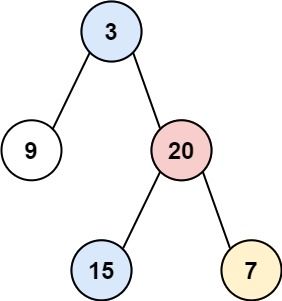
示例 1:
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
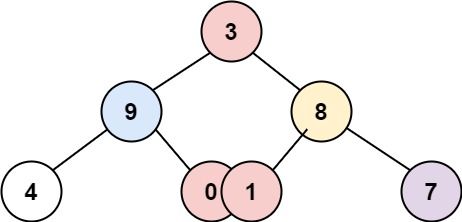
示例 2:
输入:root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7] 输出:[[4],[9],[3,0,1],[8],[7]]
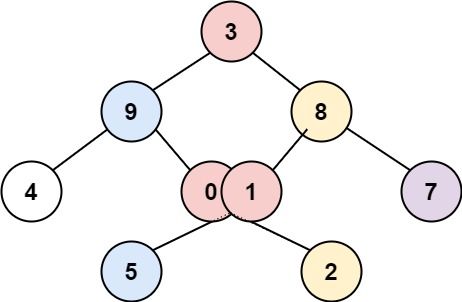
示例 3:
输入:root = [3,9,8,4,0,1,7,null,null,null,2,5] 输出:[[4],[9,5],[3,0,1],[8,2],[7]]
提示:
- 树中结点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
DFS 遍历二叉树,记录每个节点的值、深度,以及横向的偏移量。然后对所有节点按照横向偏移量从小到大排序,再按照深度从小到大排序,最后按照横向偏移量分组。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def verticalOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
def dfs(root, depth, offset):
if root is None:
return
d[offset].append((depth, root.val))
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, offset - 1)
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, offset + 1)
d = defaultdict(list)
dfs(root, 0, 0)
ans = []
for _, v in sorted(d.items()):
v.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])
ans.append([x[1] for x in v])
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeMap<Integer, List<int[]>> d = new TreeMap<>();
public List<List<Integer>> verticalOrder(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0, 0);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (var v : d.values()) {
Collections.sort(v, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();
for (var e : v) {
t.add(e[1]);
}
ans.add(t);
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, int offset) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
d.computeIfAbsent(offset, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(new int[] {depth, root.val});
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, offset - 1);
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, offset + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
using pii = pair<int, int>;
class Solution {
public:
map<int, vector<pii>> d;
vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, 0, 0);
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (auto& [_, v] : d) {
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), [&](pii& a, pii& b) {
return a.first < b.first;
});
vector<int> t;
for (auto& x : v) {
t.push_back(x.second);
}
ans.push_back(t);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int depth, int offset) {
if (!root) return;
d[offset].push_back({depth, root->val});
dfs(root->left, depth + 1, offset - 1);
dfs(root->right, depth + 1, offset + 1);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func verticalOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
d := map[int][][]int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, depth, offset int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
d[offset] = append(d[offset], []int{depth, root.Val})
dfs(root.Left, depth+1, offset-1)
dfs(root.Right, depth+1, offset+1)
}
dfs(root, 0, 0)
idx := []int{}
for i := range d {
idx = append(idx, i)
}
sort.Ints(idx)
ans := [][]int{}
for _, i := range idx {
v := d[i]
sort.SliceStable(v, func(i, j int) bool { return v[i][0] < v[j][0] })
t := []int{}
for _, x := range v {
t = append(t, x[1])
}
ans = append(ans, t)
}
return ans
}本题较好的做法应该是 BFS,从上往下逐层进行遍历。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def verticalOrder(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if root is None:
return []
q = deque([(root, 0)])
d = defaultdict(list)
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
root, offset = q.popleft()
d[offset].append(root.val)
if root.left:
q.append((root.left, offset - 1))
if root.right:
q.append((root.right, offset + 1))
return [v for _, v in sorted(d.items())]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> verticalOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return ans;
}
Deque<Pair<TreeNode, Integer>> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new Pair<>(root, 0));
TreeMap<Integer, List<Integer>> d = new TreeMap<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
var p = q.pollFirst();
root = p.getKey();
int offset = p.getValue();
d.computeIfAbsent(offset, k -> new ArrayList()).add(root.val);
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(new Pair<>(root.left, offset - 1));
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(new Pair<>(root.right, offset + 1));
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<>(d.values());
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
map<int, vector<int>> d;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q{{{root, 0}}};
while (!q.empty()) {
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
root = p.first;
int offset = p.second;
d[offset].push_back(root->val);
if (root->left) q.push({root->left, offset - 1});
if (root->right) q.push({root->right, offset + 1});
}
}
for (auto& [_, v] : d) {
ans.push_back(v);
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func verticalOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
ans := [][]int{}
if root == nil {
return ans
}
d := map[int][]int{}
q := []pair{pair{root, 0}}
for len(q) > 0 {
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
root = p.node
offset := p.offset
d[offset] = append(d[offset], root.Val)
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, pair{root.Left, offset - 1})
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, pair{root.Right, offset + 1})
}
}
}
idx := []int{}
for i := range d {
idx = append(idx, i)
}
sort.Ints(idx)
for _, i := range idx {
ans = append(ans, d[i])
}
return ans
}
type pair struct {
node *TreeNode
offset int
}