| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1939 |
Weekly Contest 370 Q3 |
|
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array values of length n, where values[i] is the value associated with the ith node.
You start with a score of 0. In one operation, you can:
- Pick any node
i. - Add
values[i]to your score. - Set
values[i]to0.
A tree is healthy if the sum of values on the path from the root to any leaf node is different than zero.
Return the maximum score you can obtain after performing these operations on the tree any number of times so that it remains healthy.
Example 1:
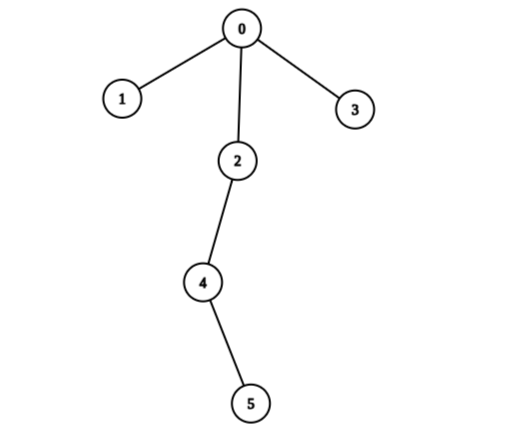
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[4,5]], values = [5,2,5,2,1,1] Output: 11 Explanation: We can choose nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. The value of the root is non-zero. Hence, the sum of values on the path from the root to any leaf is different than zero. Therefore, the tree is healthy and the score is values[1] + values[2] + values[3] + values[4] + values[5] = 11. It can be shown that 11 is the maximum score obtainable after any number of operations on the tree.
Example 2:
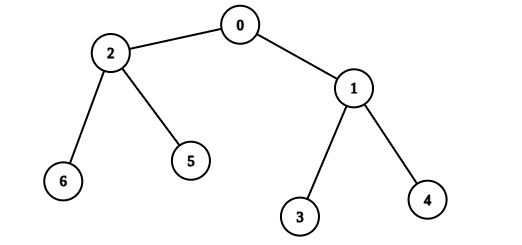
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], values = [20,10,9,7,4,3,5] Output: 40 Explanation: We can choose nodes 0, 2, 3, and 4. - The sum of values on the path from 0 to 4 is equal to 10. - The sum of values on the path from 0 to 3 is equal to 10. - The sum of values on the path from 0 to 5 is equal to 3. - The sum of values on the path from 0 to 6 is equal to 5. Therefore, the tree is healthy and the score is values[0] + values[2] + values[3] + values[4] = 40. It can be shown that 40 is the maximum score obtainable after any number of operations on the tree.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nvalues.length == n1 <= values[i] <= 109- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
The problem is actually asking us to select some nodes from all nodes of the tree so that the sum of these nodes' values is maximized, and there is one node on each path from the root node to the leaf node that is not selected.
We can use the method of tree DP to solve this problem.
We design a function
The value of
It should be noted that the value of
The answer is
The time complexity is
class Solution:
def maximumScoreAfterOperations(
self, edges: List[List[int]], values: List[int]
) -> int:
def dfs(i: int, fa: int = -1) -> (int, int):
a = b = 0
leaf = True
for j in g[i]:
if j != fa:
leaf = False
aa, bb = dfs(j, i)
a += aa
b += bb
if leaf:
return values[i], 0
return values[i] + a, max(values[i] + b, a)
g = [[] for _ in range(len(values))]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
return dfs(0)[1]class Solution {
private List<Integer>[] g;
private int[] values;
public long maximumScoreAfterOperations(int[][] edges, int[] values) {
int n = values.length;
g = new List[n];
this.values = values;
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
return dfs(0, -1)[1];
}
private long[] dfs(int i, int fa) {
long a = 0, b = 0;
boolean leaf = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
leaf = false;
var t = dfs(j, i);
a += t[0];
b += t[1];
}
}
if (leaf) {
return new long[] {values[i], 0};
}
return new long[] {values[i] + a, Math.max(values[i] + b, a)};
}
}class Solution {
public:
long long maximumScoreAfterOperations(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& values) {
int n = values.size();
vector<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].emplace_back(b);
g[b].emplace_back(a);
}
using ll = long long;
function<pair<ll, ll>(int, int)> dfs = [&](int i, int fa) -> pair<ll, ll> {
ll a = 0, b = 0;
bool leaf = true;
for (int j : g[i]) {
if (j != fa) {
auto [aa, bb] = dfs(j, i);
a += aa;
b += bb;
leaf = false;
}
}
if (leaf) {
return {values[i], 0LL};
}
return {values[i] + a, max(values[i] + b, a)};
};
auto [_, b] = dfs(0, -1);
return b;
}
};func maximumScoreAfterOperations(edges [][]int, values []int) int64 {
g := make([][]int, len(values))
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
var dfs func(int, int) (int64, int64)
dfs = func(i, fa int) (int64, int64) {
a, b := int64(0), int64(0)
leaf := true
for _, j := range g[i] {
if j != fa {
leaf = false
aa, bb := dfs(j, i)
a += aa
b += bb
}
}
if leaf {
return int64(values[i]), int64(0)
}
return int64(values[i]) + a, max(int64(values[i])+b, a)
}
_, b := dfs(0, -1)
return b
}function maximumScoreAfterOperations(edges: number[][], values: number[]): number {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: values.length }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
const dfs = (i: number, fa: number): [number, number] => {
let [a, b] = [0, 0];
let leaf = true;
for (const j of g[i]) {
if (j !== fa) {
const [aa, bb] = dfs(j, i);
a += aa;
b += bb;
leaf = false;
}
}
if (leaf) {
return [values[i], 0];
}
return [values[i] + a, Math.max(values[i] + b, a)];
};
return dfs(0, -1)[1];
}