-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
1 parent
4fdee3b
commit 5d06a84
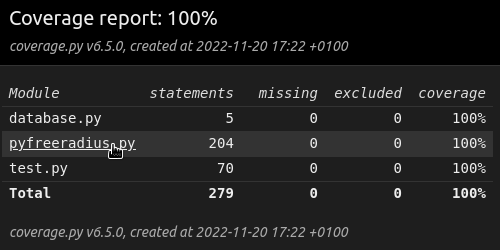
Showing
1 changed file
with
97 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -472,6 +472,103 @@ The HTML report is then browsable: | |
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| # API authentication (optional) | ||
|
|
||
| You may want to add authentication to the API. | ||
|
|
||
| ## TL;DR | ||
|
|
||
| A simple solution is through API key. | ||
| Only two steps are required this way: | ||
|
|
||
| * Create `src/auth.py`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```py | ||
| from fastapi import Depends, HTTPException | ||
| from fastapi.security.api_key import APIKeyHeader | ||
|
|
||
| _x_api_key = 'my-valid-key' | ||
| _x_api_key_header = APIKeyHeader(name='X-API-Key') | ||
|
|
||
| async def verify_key(x_api_key: str = Depends(_x_api_key_header)): | ||
| if x_api_key != _x_api_key: | ||
| raise HTTPException(401, 'Invalid key') | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| * Apply following changes in `src/api.py`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```diff | ||
| # top of the file | ||
| +from auth import verify_key | ||
| +from fastapi import Depends | ||
|
|
||
| # bottom of the file | ||
| -app = FastAPI(title='FreeRADIUS REST API') | ||
| +app = FastAPI(title='FreeRADIUS REST API', dependencies=[Depends(verify_key)]) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| That's it! All endpoints now require authentication. | ||
|
|
||
| > In the above code, we make use of both [global dependencies](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/dependencies/global-dependencies/) and [security](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/security/first-steps/) features of FastAPI. API key is not properly documented yet but the issue https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues/142 provides some working snippets. | ||
| > The key would not normally go "in the clear" in the code like this. Depending on your setup, it would be passed using CI/CD variables for example. | ||
| ## Demo | ||
|
|
||
| ### Using `curl` | ||
|
|
||
| ```sh | ||
| $ curl -X 'GET' -i http://localhost:8000/users | ||
| HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden | ||
|
|
||
| {"detail":"Not authenticated"} | ||
| ``` | ||
| ```sh | ||
| $ curl -X 'GET' -H 'X-API-Key: an-invalid-key' -i http://localhost:8000/users | ||
| HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized | ||
|
|
||
| {"detail":"Invalid key"} | ||
| ``` | ||
| ```sh | ||
| $ curl -X 'GET' -H 'X-API-Key: my-valid-key' -i http://localhost:8000/users | ||
| HTTP/1.1 200 OK | ||
|
|
||
| ["bob","alice@adsl","eve","[email protected]"] | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### Using the Web UI | ||
|
|
||
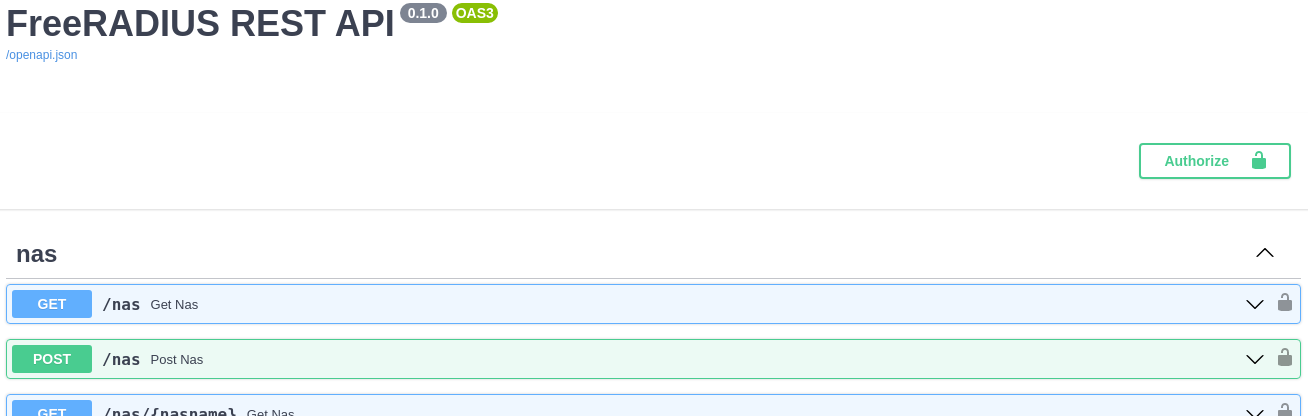
| Because the API key security scheme is part of the [OpenAPI specification](https://swagger.io/specification/#security-scheme-object), the need for authentication gets specified on the Web UI 😊 | ||
|
|
||
| * You will now notice an `Authorize` button at the top-right corner as well as a little lock on each endpoint: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
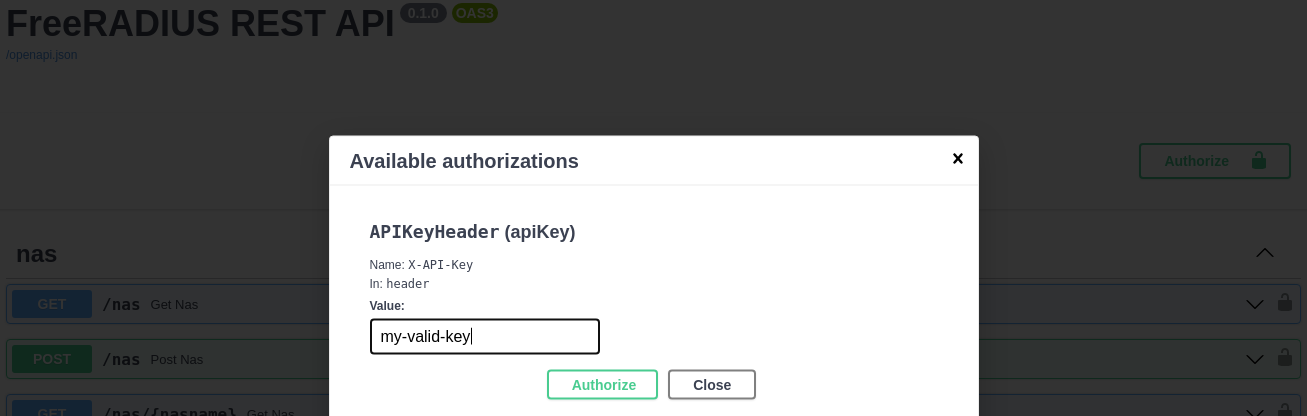
| * To play with the API, you first need to provide the key by clicking that `Authorize` button: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
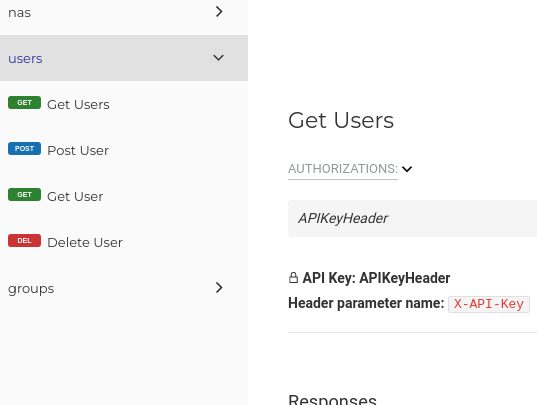
| * Alternatively, on the Redoc Web UI: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## Explanation | ||
|
|
||
| FastAPI supports multiple security schemes, including OAuth2, API key and others. OAuth2 is a vast subject and will not be treated here. API key is a simple mechanism you probably already used in some projects. The [Swagger doc](https://swagger.io/docs/specification/authentication/api-keys/) explains it very well: | ||
|
|
||
| > **An API key is a token that a client provides when making API calls.** The key can be sent in the query string or as a request header or as a cookie. API keys are supposed to be a secret that only the client and server know. Like Basic authentication, **API key-based authentication is only considered secure if used together with other security mechanisms such as HTTPS/SSL.** | ||
| A request header is quite common. Some examples: | ||
|
|
||
| * `X-API-Key: <TOKEN>` (as per the Swagger doc and the one I used in the solution) | ||
| * `X-Auth-Token: <TOKEN>` (e.g., LibreNMS) | ||
| * `Authorization: Token <TOKEN>` (e.g., NetBox and [DjangoREST-based projects](https://github.com/encode/django-rest-framework/blob/3.14.0/rest_framework/authentication.py#L151-L161) more generally) | ||
| * `Authorization: Bearer <TOKEN>` (in accordance with [RFC 6750](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6750#section-2.1) of the OAuth2 framework) | ||
|
|
||
| > The `X-` prefix denotes a non-standard HTTP header. You can set whatever name you prefer after that `X-`. The associated semantic is up to you. Some interesting background about the `X-` convention can be found in [RFC 6648](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6648#appendix-A) which, by the way, officially deprecates it. | ||
| > Although `Authorization: Token` seems more standard as it follows [RFC 2617](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc2617) syntax, note the `Token` authentication scheme is not part of the [IANA HTTP Authentication Scheme Registry](https://www.iana.org/assignments/http-authschemes/http-authschemes.xhtml) so it is still custom in a sense. The only true standard header is `Authorization: Bearer` introduced by the OAuth2 framework. | ||
| # Conceptual approach | ||
|
|
||
| You may be interested in the model-centric approach taken (or you may not). | ||
|
|
||