This project is about understanding what processes and pipes are and how they work and this documentation should give you the basics and help you start the project.
- You must create a program that act exactly as bash:
< infile cmd[1] | cmd[2] > outfile- Your program must only take 4 parameters as follows:
./pipex infile cmd[1] cmd[2] outfile- The Bonus part is about multiple pipes and reproducing the HERE_DOC behavior so it should work like:
< infile cmd[1] | ... | cmd[n] > outfileor:
<< LIMITER cmd[1] | ... | cmd[n] >> outfile- Your program will be called as:
./pipex_bonus infile cmd[1] ... cmd[n] outfileor :
./pipex_bonus here_doc LIMITER cmd[1] ... cmd[n] outfileCheck out the subject for more understanding. here.
A process is basically a program in execution, To put it in simple terms, we write our computer programs in a text file and when we execute this program, it becomes a process which performs all the tasks mentioned in the program, when a program is loaded into the memory and it becomes a process.
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Start | This is the initial state when a process is first started/created. |
| Ready | The process is waiting to be assigned to a processor. Ready processes are waiting to have the processor allocated to them by the operating system so that they can run. Process may come into this state after Start state or while running it by but interrupted by the scheduler to assign CPU to some other process. |
| Running | Once the process has been assigned to a processor by the OS scheduler, the process state is set to running and the processor executes its instructions. |
| Waiting | Process moves into the waiting state if it needs to wait for a resource, such as waiting for user input, or waiting for a file to become available. |
| Terminated | Once the process finishes its execution, or it is terminated by the operating system, it is moved to the terminated state where it waits to be removed from main memory. |
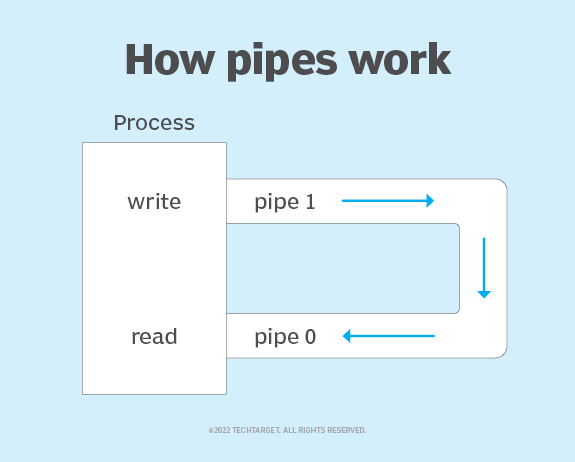
In computer programming, a pipe is a technique for passing information from one process to another in a oneway direction.
The pipe works by creating a buffer in the kernel and returning two file descriptors (FDs) that refer to it.
This project was done by jaguar-ks: