forked from Asiatik/codezilla
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
* Fix Asiatik#87: Added Documentation for Insertion Sort Added a README.md * Delete README.md * Fix Asiatik#87: Added Documentation for Insertion Sort Fix Asiatik#87: Added Documentation for Insertion Sort
- Loading branch information
1 parent
fab212e
commit 9f3642a
Showing
1 changed file
with
18 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,18 @@ | ||
| # Insertion Sort | ||
| Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that builds the final sorted array (or list) one item at a time. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort. However, insertion sort provides several advantages: | ||
| - Simple implementation: Jon Bentley shows a three-line C version, and a five-line optimized version[2] | ||
| - Efficient for (quite) small data sets, much like other quadratic sorting algorithms | ||
| - More efficient in practice than most other simple quadratic (i.e., O(n2)) algorithms such as selection sort or bubble sort | ||
| - Adaptive, i.e., efficient for data sets that are already substantially sorted: the time complexity is O(nk) when each element in the input is no more than k places away from its sorted position | ||
| - Stable; i.e., does not change the relative order of elements with equal keys | ||
| - In-place; i.e., only requires a constant amount O(1) of additional memory space | ||
| - Online; i.e., can sort a list as it receives it | ||
| # | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
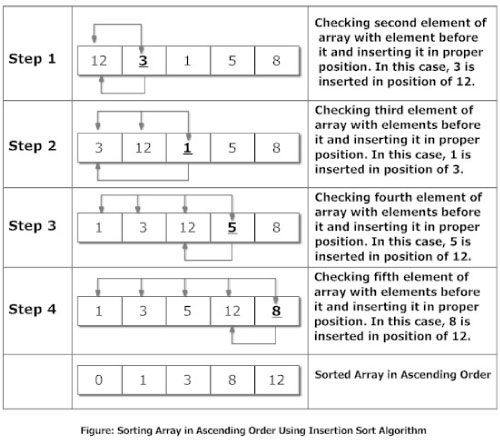
| ### Explanation | ||
| Suppose, you want to sort elements in ascending as in above figure. Then: | ||
| - Step 1: The second element of an array is compared with the elements that appears before it (only first element in this case). If the second element is smaller than first element, second element is inserted in the position of first element. After first step, first two elements of an array will be sorted. | ||
| - Step 2: The third element of an array is compared with the elements that appears before it (first and second element). If third element is smaller than first element, it is inserted in the position of first element. If third element is larger than first element but, smaller than second element, it is inserted in the position of second element. If third element is larger than both the elements, it is kept in the position as it is. After second step, first three elements of an array will be sorted. | ||
| - Step 3: Similary, the fourth element of an array is compared with the elements that appears before it (first, second and third element) and the same procedure is applied and that element is inserted in the proper position. After third step, first four elements of an array will be sorted. |