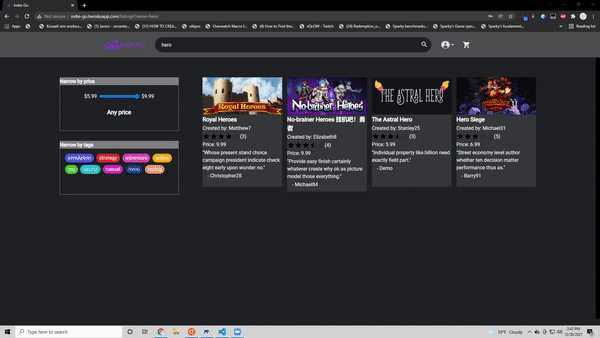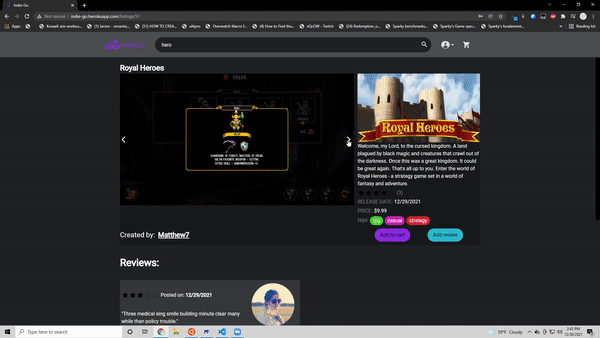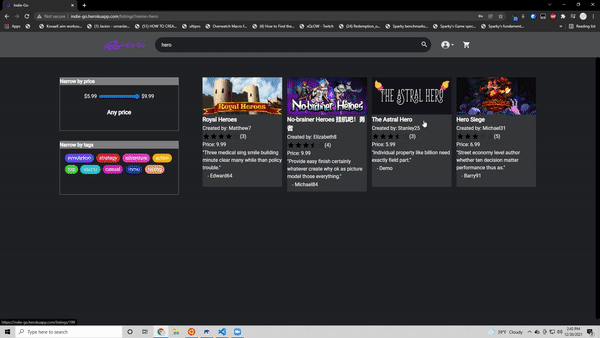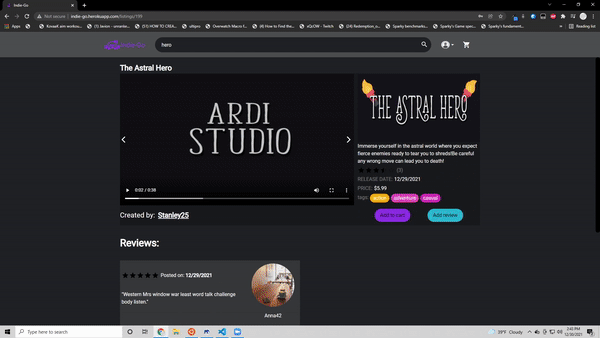
Since this was hosted on heroku this is currently down. Working on making a next.js version and hosting it on vercel! Below you can see information from the site when it was still up and running
Table of contents
Indie-Go is a fullstack web-app using React, React-Redux, Python/Flask and PostgreSQL
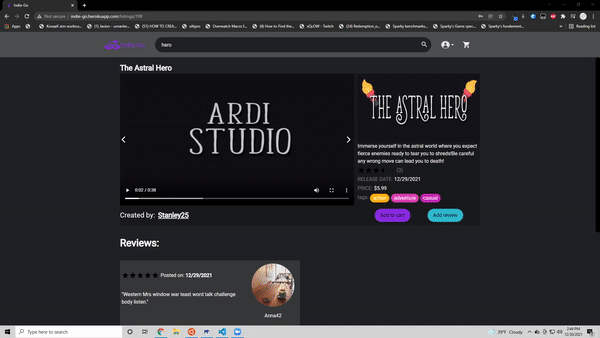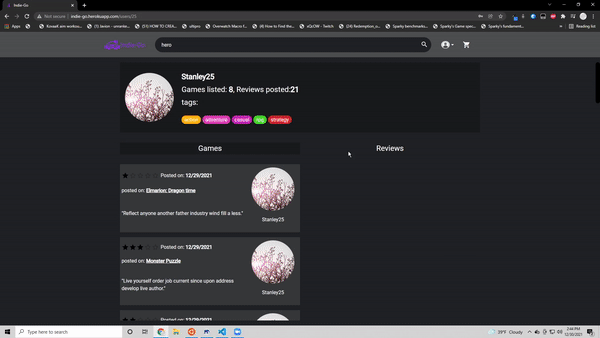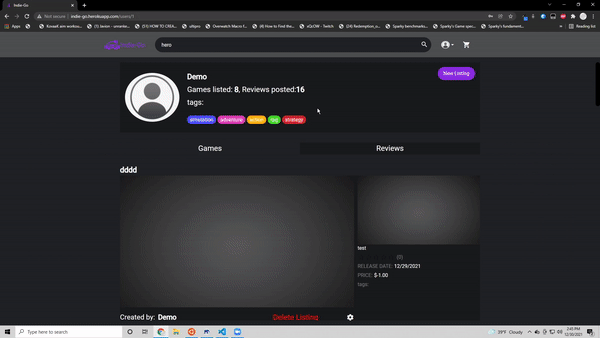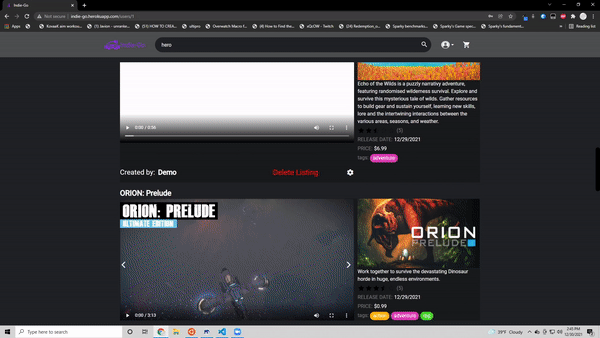
This app is a combination of Etsy and Steam specifically for indie games.
Users are able to:
- Search through 400 pre seeded games from Steams's API
- Create, update and delete their own game listing
- Create, update and delete reviews on game listings
- Add, remove games to the user's cart
- Checkout with the games in the user's cart
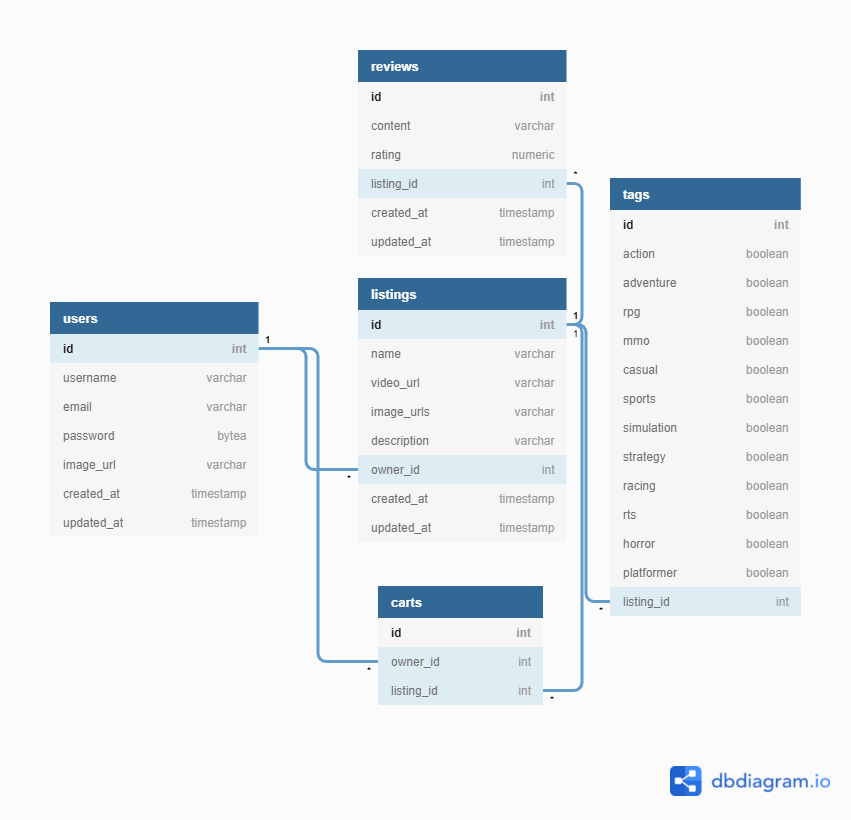
Database (PostgreSQL)
The database for this app was set up to communicate with the server to store data for persistance between sessions and to serve back that data for games, listings and user cart details
SQLAlchemy was used to create models to easily store and harvest data from the database.
Game listing model:
# in /app/models/listing.py
class Listing(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'listings'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False)
video_url = db.Column(db.String(255), nullable=True)
image_urls = db.Column(db.Text(), nullable=False)
description = db.Column(db.String(500), nullable=True)
price = db.Column(db.Numeric(6, 2), nullable=True)
owner_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey(
'users.id'), nullable=False)
created_at = db.Column(db.DateTime(), nullable=False,
server_default=func.now())
updated_at = db.Column(
db.DateTime(), onupdate=func.now(), default=func.now())
users = db.relationship('User', back_populates='listings')
reviews = db.relationship(
'Review', back_populates='listings', cascade="all, delete")
tags = db.relationship(
'Tag', back_populates='listings', cascade="all, delete")
cart_owners = db.relationship(
"User",
secondary='cart_listings',
back_populates="listings",
overlaps="cart_listings"
)
def owner(self):
return self.users.to_dict()
def listingId(self):
return self.id
def listingInfo(self):
return {
'name': self.name,
'video_url': self.video_url,
'image_urls': json.loads(self.image_urls.replace("'", '"')),
'description': self.description,
"price": str(self.price),
'owner_id': self.owner_id,
}
def to_dict(self):
reviews = [review.to_dict() for review in self.reviews]
return {
'id': self.id,
'name': self.name,
'video_url': self.video_url,
'image_urls': json.loads(self.image_urls.replace("'", '"')),
'description': self.description,
"price": str(self.price),
'owner_id': self.owner_id,
'owner': self.users.info(),
'tags': self.tags[0].to_list() if self.tags else [],
'reviews': reviews,
'created_at': self.created_at.strftime('%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S'),
'updated_at': self.updated_at.strftime('%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S')
}
Server (Python/Flask)
The server for this app was coded using python with Flask to create routes responsible for dataflow between the frontend and the database.
Listing POST route (images uploaded to and hosted on AWS):
# in app/api/listing_routes
@listing_routes.route('/', methods=['POST'])
@login_required
def postListing():
form = ListingForm()
form['csrf_token'].data = request.cookies['csrf_token']
video = form.data["video"]
videoURL = None
if video:
video.filename = get_unique_filename(video.filename)
videoupload = upload_file_to_s3(video)
videoURL = videoupload["url"]
uploads = [form.data["image1"], form.data["image2"],
form.data["image3"], form.data["image4"], form.data["image5"]]
imageURLs = []
for upload in uploads:
if upload:
upload.filename = get_unique_filename(upload.filename)
imageupload = upload_file_to_s3(upload)
imageURLs.append(imageupload["url"])
listing = Listing(
name=form.data["name"],
description=form.data["description"],
video_url=videoURL,
image_urls=json.dumps(imageURLs),
price=form.data["price"],
owner_id=current_user.id
)
db.session.add(listing)
db.session.commit()
tagsList = json.loads(form.data["tags"])
tags = Tag(
**tagsList,
listing_id=listing.listingId()
)
db.session.add(tags)
db.session.commit()
return listing.to_dict()React (React)
The front end of Indie-Go is all based in react. React is one of the most popular JS frameworks for full stack aplications. Using React Components with Redux state Indie-Go serves all the data from the backend to be viewed by the user.
// in react-app/src/components/User/index.js
function User({ user }) {
const session = useSelector((state) => state.session);
if (!user) {
return null;
}
let listings = user?.listings;
let tags = new Set(listings?.flatMap((listing) => listing.tags));
return (
<div className={style.container}>
<img src={user?.image_url} alt="" />
<span>
<strong>{user?.username}</strong>
</span>
<span>
Games listed: <strong>{listings?.length}</strong>, Reviews posted:
<strong>{user?.reviews?.length}</strong>
</span>
<span>tags:</span>
<div className={style.tags}>
{[...tags].map((tag, i) => (
<span key={i} className={"tags " + tag}>
{tag}
</span>
))}
</div>
{session?.user?.id === +user?.id && (
<Link className="primary-link" to={`/users/${user.id}/listings/new/1`}>
New Listing
</Link>
)}
</div>
);
}
export default User;Redux Store (React-Redux)
Redux is used to keep a site wide state for the current logged in user and all game listings. On application start Redux stores all listings, while this causes initial load time to be longer it allows for a fast experience with game listings after initial load.
Part of the Redux state tree (1 and 2 are game listings):
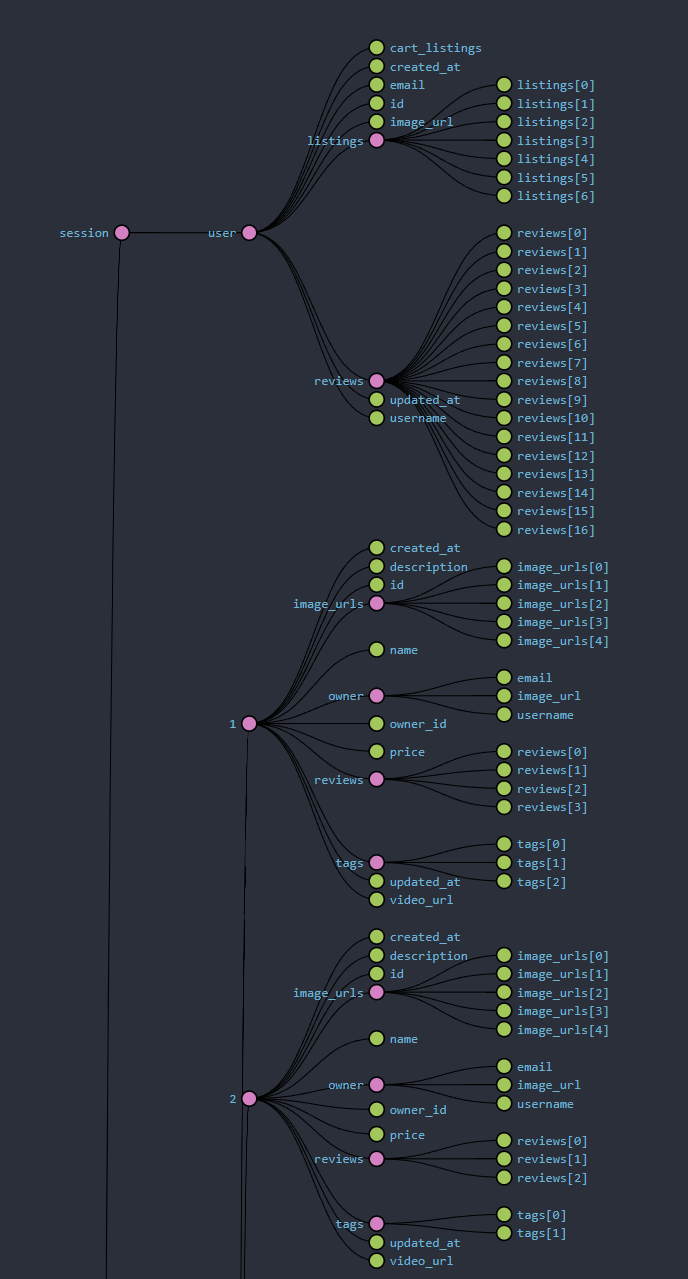
Redux uses Thunks to communicate to the backend and then change state with an Action based on the response
Thunk for POST listing:
// in react-app/src/store/listings.js
export const postListing =
(video, images, name, description, price, tags) => async (dispatch) => {
const formData = new FormData();
if (video) formData.append("video", video);
images.map((image, i) =>
image ? formData.append(`image${i + 1}`, image) : null
);
formData.append("name", name);
formData.append("description", description);
formData.append("tags", JSON.stringify(tags));
if (price) formData.append("price", price);
const res = await fetch("/api/listings/", {
method: "POST",
body: formData,
});
const data = await res.json();
dispatch(post(data));
};Action dispatched with data from the response from server:
// in react-app/src/store/listings.js
const post = (listing) => ({
type: POST,
listing,
});