-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 99
RoadTrafficModel
This tutorial has for goal to present the use of GIS data and complex geometries. In particular, this tutorial shows how to load gis data, to agentify them and to use a network of polylines to constraint the movement of agents. All the files related to this tutorial (shapefiles and models) are available in the Library models (Tutorials, Road Traffic).
If you are not familiar with agent-based models or GAMA, we advise you to have a look at the prey-predator model first.
The model built in this tutorial concerns the study of road traffic in a small city. Two layers of GIS data are used: a road layer (polylines) and a building layer (polygons). The building GIS data contain an attribute: the 'NATURE' of each building: a building can be either 'Residential' or 'Industrial'. In this model, people agents are moving along the road network. Each morning, they are going to an industrial building to work, and each night they are coming back home. Each time a people agent takes a road, it wears it out. More a road is worn out, more a people agent takes time to go all over it. The town council is able to repair some roads.
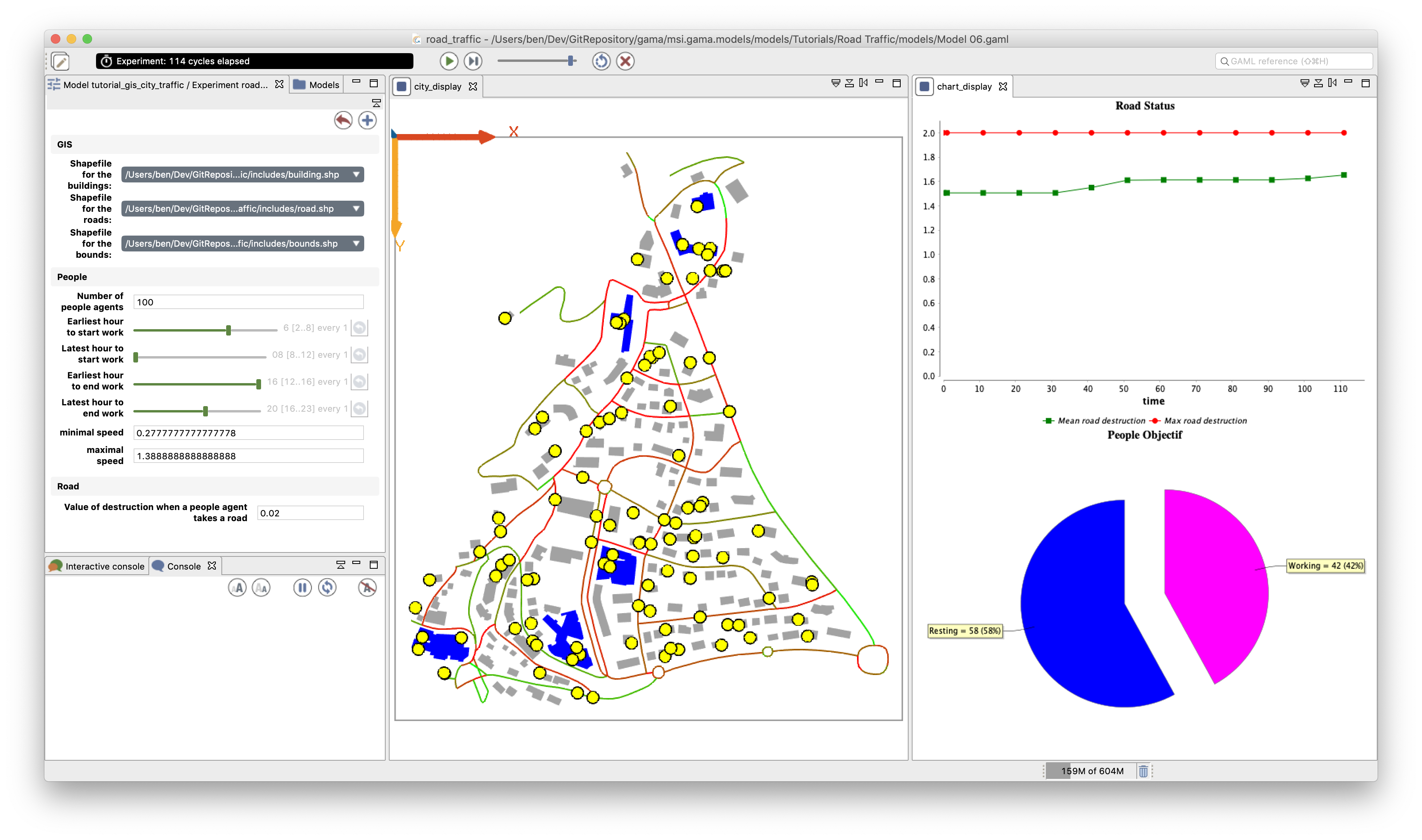
This tutorial is composed of 7 steps corresponding to 7 models which are incremental representation of the same model, starting with the simplest model 1 and finishing with the latest one, model 7. For each step, we will present its purpose, an explicit formulation, and the corresponding GAML code.
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Model Section
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation